AAV6-mediated shRNA with mCherry expression (From
BrainVTA)was used to perform in vivo knockdown of sortilin in L5 DRG to evaluate whether changes in sortilin expression were required for pain hypersensitivity.
The viruses used in this article from BrainVTA are in the table below
|
Custom-Made AAVs |
rAAV-U6-BBSI-shRNA-CMV-mCherry-pA |
|
rAAV-U6-shRNA2-Sort1-CMV-mCherry |
Idy H.T. Ho, Xiaodong Liu, Yidan Zou, Taian Liu, Wei Hu, Hung Chan, Yuanyuan Tian, Yuchen, Zhang, Qing Li, Shanglong Kou, Chee Sam Chan, Tony Gin, Christopher H.K. Cheng, Sunny H. Wong, Jun Yu, Lin Zhang, William K.K. Wu, Matthew T.V. Chan
Pub Date: 2019-02-28,
DOI: 10.7150/thno.29703,
Email: [email protected]
Rationale: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a key mediator in the development of chronic pain. Sortilin is known to interact with proBDNF and regulate its activity-dependent secretion in cortical neurons. In a rat model of inflammatory pain with intraplantar injection of complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA), we examined the functional role of proBDNF-sortilin interaction in dorsal root ganglia (DRG).
Methods: Expression and co-localization of BDNF and sortilin were determined by immunofluorescence. ProBDNF-sortilin interaction interface was mapped using co-immunoprecipitation and bimolecular fluorescence complementation assay. The analgesic effect of intrathecal injection of a synthetic peptide interfering with proBDNF-sortilin interaction was measured in the CFA model.
Results: BDNF and sortilin were co-localized and their expression was significantly increased in ipsilateral L4/5 DRG upon hind paw CFA injection. In vivo adeno-associated virus-mediated knockdown of sortilin-1 in L5 DRG alleviated pain-like responses. Mapping by serial deletions in the BDNF prodomain indicated that amino acid residues 71-100 supported the proBDNF-sortilin interaction. A synthetic peptide identical to amino acid residues 89-98 of proBDNF, as compared with scrambled peptide, was found to interfere with proBDNF-sortilin interaction, inhibit activity-dependent release of BDNF in vitro and reduce CFA-induced mechanical allodynia and heat hyperalgesia in vivo. The synthetic peptide also interfered with capsaicin-induced phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases in ipsilateral spinal cord of CFA-injected rats.
Conclusions: Sortilin-mediated secretion of BDNF from DRG neurons contributes to CFA-induced inflammatory pain. Interfering with proBDNF-sortilin interaction reduced activity-dependent release of BDNF and might serve as a therapeutic approach for chronic inflammatory pain.
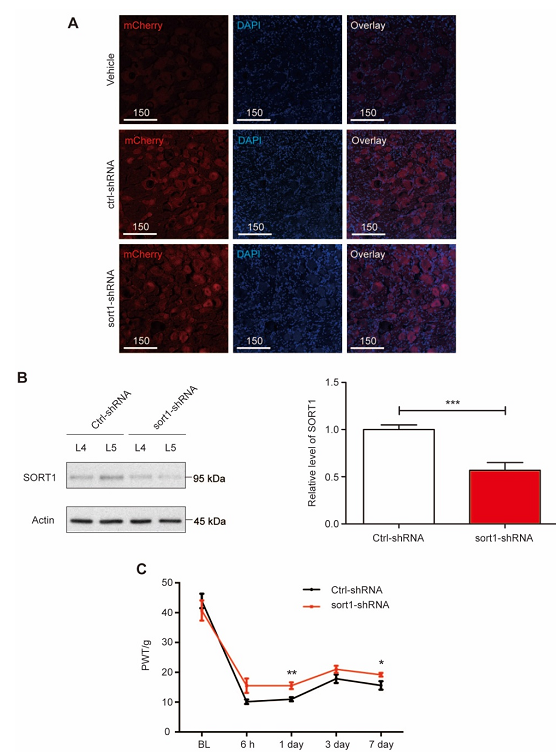 Figure. 1 L5 DRG-specific knockdown of sortilin alleviated inflammatory-induced chronic pain.
Figure. 1 L5 DRG-specific knockdown of sortilin alleviated inflammatory-induced chronic pain.
The authors want to elucidate the exact regulatory mechanism when Endogenous BDNF from primary sensory neurons was released in an activity-dependent manner. The results showed sortilin-mediated secretion of BDNF from DRG neurons contributes to CFA-induced inflammatory pain. Interfering with proBDNF-sortilin interaction reduced activity-dependent release of BDNF and might serve as a therapeutic approach for chronic inflammatory pain.
BrainVTA offers viral vector construction & virus packaging services for AAV, LV, RABV, PRV, HSV and VSV that help researchers explore questions about genes, neurons, circuitry structure, function of brain network, mechanism and treatment of diseases.
If you have any needs, just email us at
[email protected].
