hM3D(Gq)-mCherry and hM4D(Gi)-mCherry (From
BrainVTA) were used for chemogenetic activation or inhibition of GABAergic neurons in vlPAG.
The viruses used in this article from BrainVTA are in the table below
|
CRE Recombinase |
PT-0306 rAAV-mDlx-CRE-WPRE-pA |
|
Chemogenetics |
PT-0019 rAAV-hSyn-DIO-hM3D(Gq)-mCherry-WPRE-pA
PT-0020 rAAV-hSyn-DIO-hM4D(Gi)-mCherry-WPRE-pA
PT-0123 rAAV-CaMKIIa-HA-KORD-IRES-mCitrine-WPRE-pA |
|
Control |
PT-0100 rAAV-hSyn-mCherry-WPRE-pA |
He Zhu, Hong-Chun Xiang, Hong-Ping Li, Li-Xue Lin, Xue-Fei Hu, Hong Zhang, Wang-Yang Meng, Lu Liu, Chao Chen, Yang Shu, Ru-Yue Zhang, Pei Zhang, Jun-Qiang Si and Man Li
Pub Date: 2019-05-17,
DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00484,
Email: [email protected]
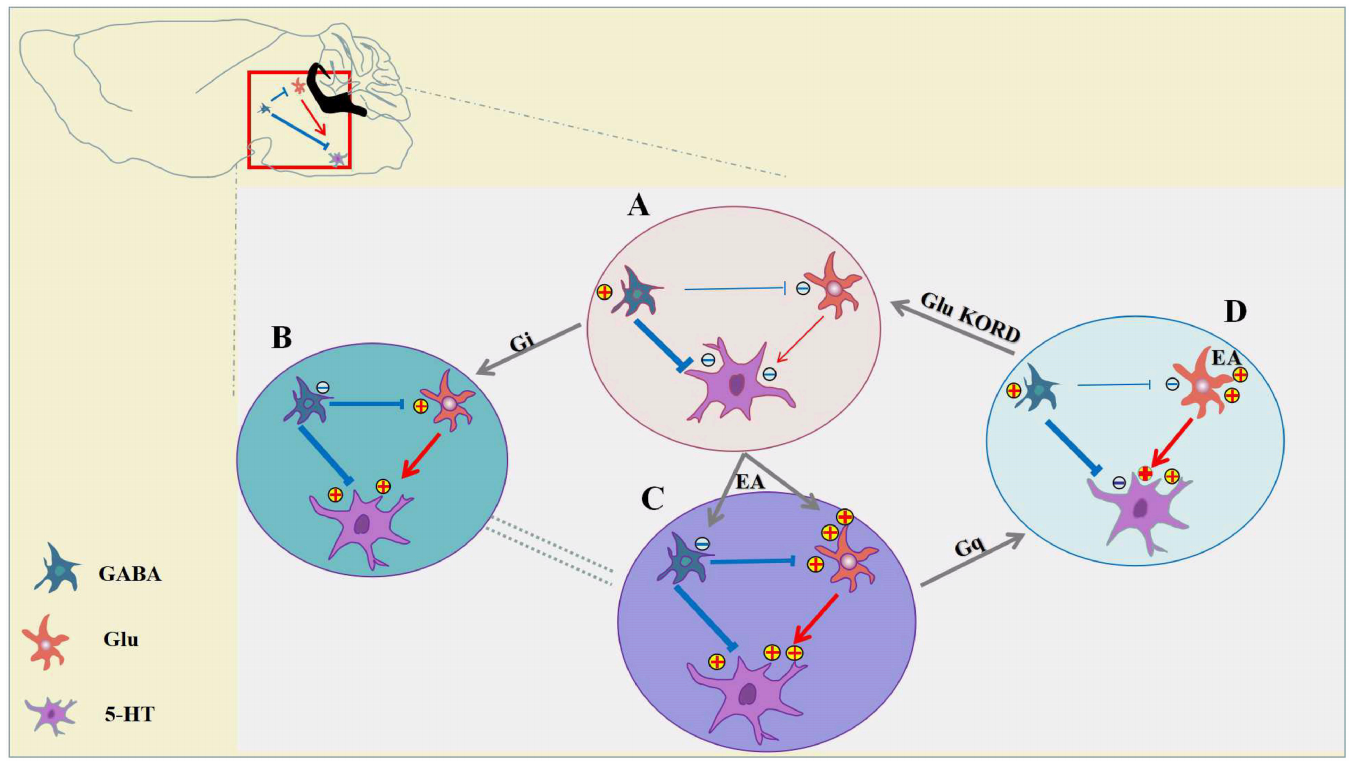
Although electroacupuncture (EA) has become a worldwide practice, little is understood about its precise target in the central nervous system (CNS) and the cell type-specific analgesia mechanism. In the present study, we found that EA has significant antinociceptive effects both in inflammatory and neuropathic pain models. Chemogenetic inhibition of GABAergic neurons in the ventrolateral periaqueductal gray (vlPAG) replicated the effects of EA, whereas the combination of chemogenetic activation of GABAergic neurons and chemogenetic inhibition of glutamatergic neurons in the vlPAG was needed to reverse the effects of EA. Specifically knocking out CB1 receptors on GABAergic neurons in the vlPAG abolished the EA effect on pain hypersensitivity, while specifically knocking out CB1 receptors on glutamatergic neurons attenuated only a small portion of the EA effect. EA synchronously inhibits GABAergic neurons and activates glutamatergic neurons in the vlPAG through CB1 receptors to produce EA-induced analgesia. The CB1 receptors on GABAergic neurons localized in the vlPAG was the basis of the EA effect on pain hypersensitivity. This study provides new experimental evidence that EA can bidirectionally regulate GABAergic neurons and glutamatergic neurons via the CB1 receptors of the vlPAG to produce analgesia effects.
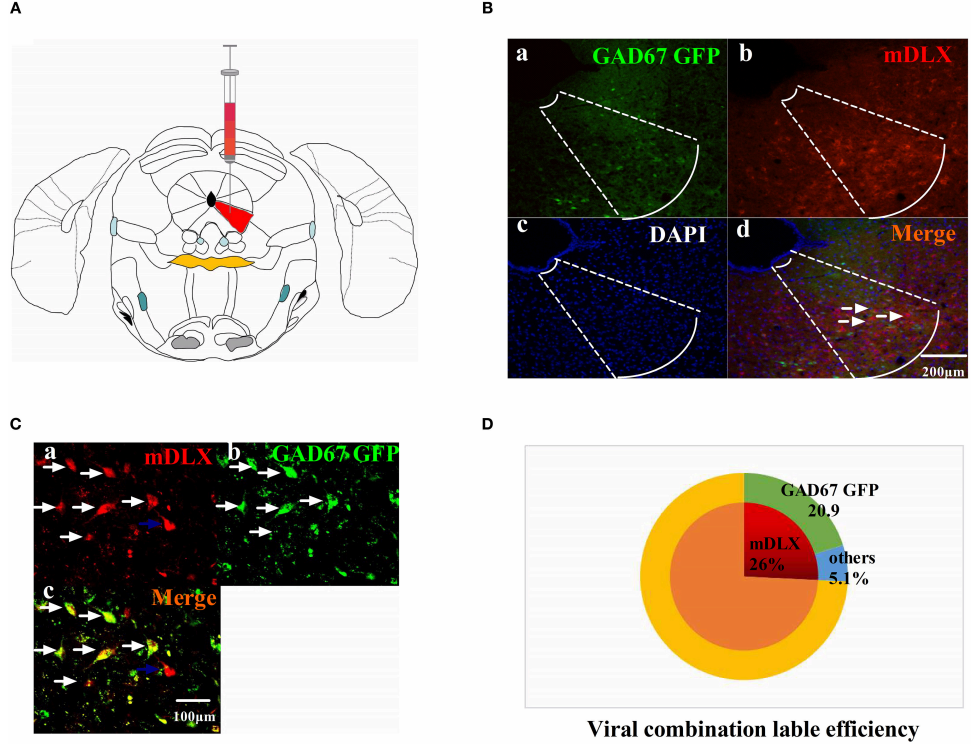 Figure. 1 The viruses combination cocktail label efficiency.
Figure. 1 The viruses combination cocktail label efficiency.
In this study, with the help of cell type-specific chemogenetic manipulations(From
BrainVTA) in the vlPAG, the authors attempt to verify the hypothesis that GABAergic neurons and glutamatergic neurons are involved in CB1-mediated EA antinociception. They provided new experimental evidence that chemogenetic inhibition of GABAergic neurons in the vlPAG was able to replicate the antinociceptive effect of EA and accordingly further verify that the vlPAG is essential for EA analgesia.
BrainVTA offers viral vector construction & virus packaging services for AAV, LV, RABV, PRV, HSV and VSV that help researchers explore questions about genes, neurons, circuitry structure, function of brain network, mechanism and treatment of diseases.
If you have any needs, just email us at
[email protected].

