SFV-EGFP (From
BrainVTA) to sparsely label neurons was used examined the dendritic processes and spines of ACC pyramidal neurons. EYFP viruses for optical activation behavioral experiments, hM3D(Gq) viruses for the DREADDs activation behavioral experiments and virus containing SaCas9 for the conditional knockout and rescue experiments were used to explore the role of ACC in the regulation of social behavior.
The viruses used in this article from BrainVTA are in the table below
|
Semliki Forest virus |
SFV-EGFP |
Pub Date: 2019-07-22,
DOI: 10.1038/s41593-019-0445-9. Email: [email protected]
Baolin Guo , Jing Chen, Qian Chen, Keke Ren, Dayun Feng, Honghui Mao, Han Yao, Jing Yang, Haiying Liu, Yingying Liu, Fan Jia, Chuchu Qi, Taylor Lynn-Jones, Hailan Hu , Zhanyan Fu, Guoping Feng , Wenting Wang and Shengxi Wu
Social deficit is a core clinical feature of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) but the underlying neural mechanisms remain largely unclear. We demonstrate that structural and functional impairments occur in glutamatergic synapses in the pyramidal neurons of the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) in mice with a mutation in Shank3, a high-confidence candidate ASD gene. Conditional knockout of Shank3 in the ACC was sufficient to generate excitatory synaptic dysfunction and social interaction deficits, whereas selective enhancement of ACC activity, restoration of SHANK3 expression in the ACC, or systemic administration of an α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid receptor-positive modulator improved social behavior in Shank3 mutant mice. Our findings provide direct evidence for the notion that the ACC has a role in the regulation of social behavior in mice and indicate that ACC dysfunction may be involved in social impairments in ASD.
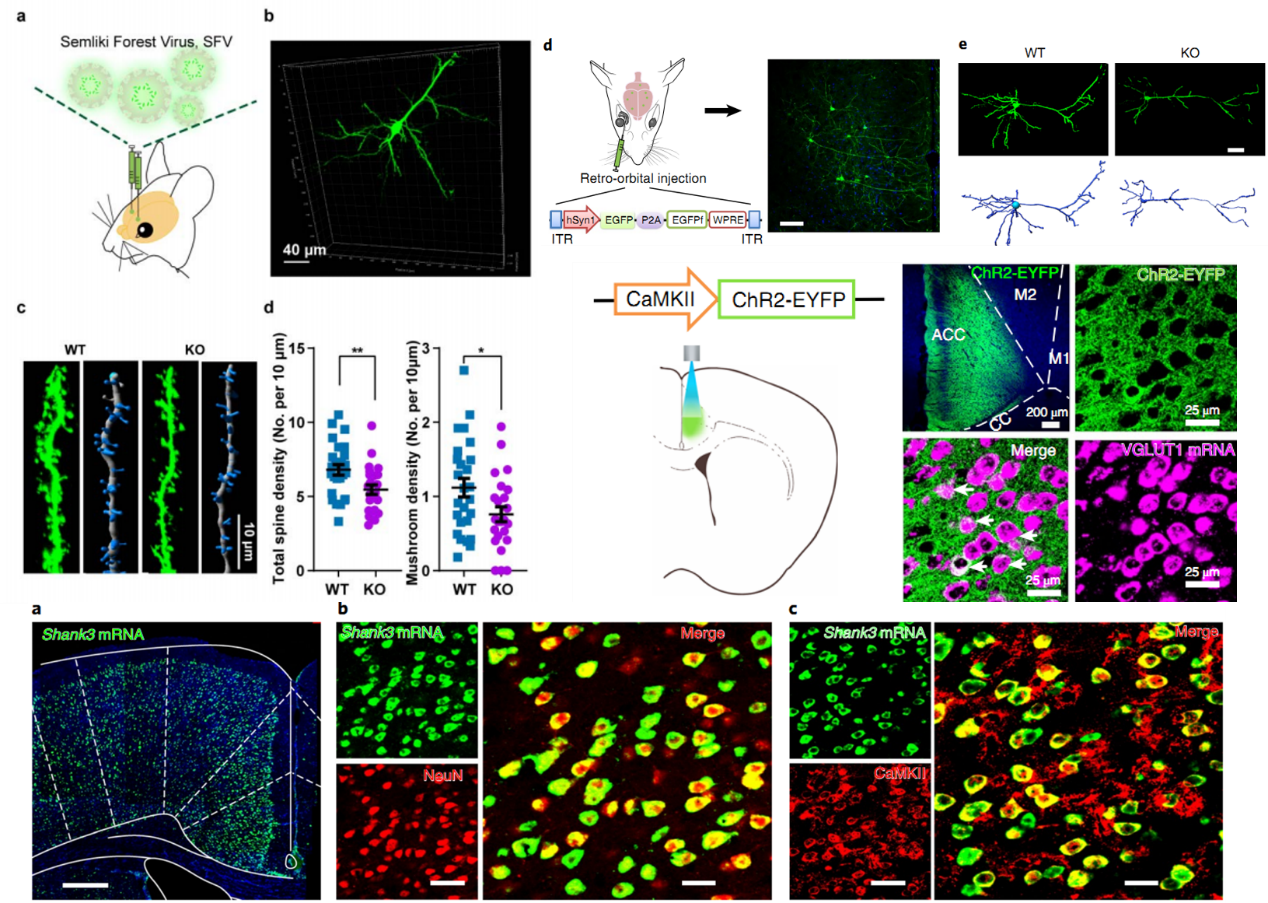 Fig.1 Using SFV and AAV viruses to explore the role of ACC in the regulation of social behavior.
Fig.1 Using SFV and AAV viruses to explore the role of ACC in the regulation of social behavior.
To determine whether the Shank3 deletion would induce structural and functional changes in the pyramidal neurons of the ACC, the researchers used local injections of Semliki Forest virus (SFV) (From
BrainVTA) to sparsely label neurons with green fluorescent protein (GFP) in wild-type (WT) and Shank3 KO mice. The results showed that the deletion of Shank3 leads to structural defects in the dendrites and spines of ACC pyramidal neurons by electron microscopy.
BrainVTA offers viral vector construction & virus packaging services for AAV, LV, RABV, PRV, HSV and VSV that help researchers explore questions about genes, neurons, circuitry structure, function of brain network, mechanism and treatment of diseases.
If you have any needs, just email us at
[email protected].
